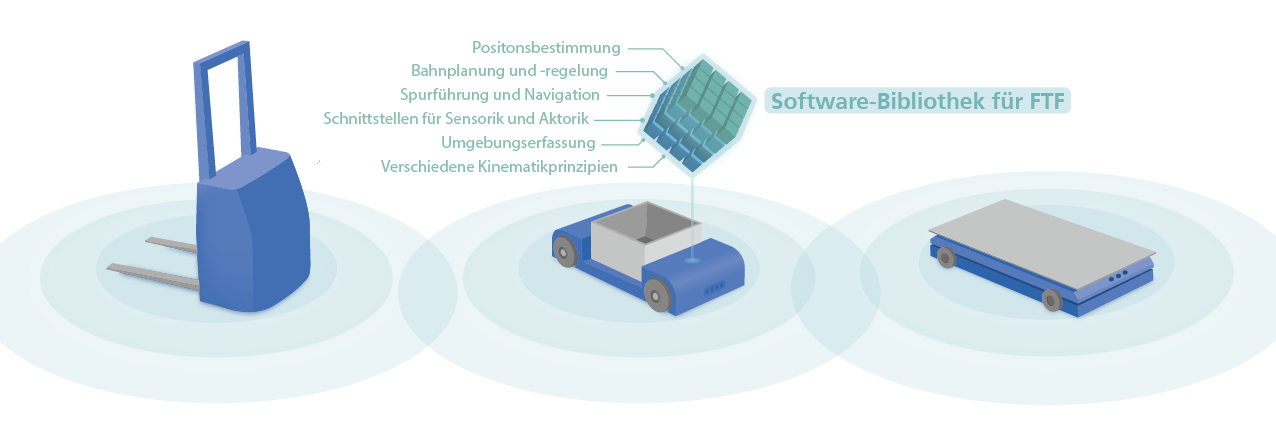
The Navigation controller of Fraunhofer IML
Contrary to its name, the navigation controller is not only hardware, but essentially a very extensive and powerful software library for the control of Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) - which of course also requires hardware (a controller / IPC) on which it is running. The software is intended to work as a supplement to an existing vehicle controller (this usually is a simple PLC). It enables to automatically drive an AGV without physical track guidance (optical/magnetic/inductive guideline). This means the AGV can run free of physical constraints on a so-called virtual guideline and is therefore considerably more flexible than before.
Line guidance, laser navigation and hybrid navigation
The software modules for position determination, path planning and path control, that are required for such a virtual guidance system are available, as are the interfaces required for operation with different localization sensors or locating systems. In addition to the method of odometry/dead reckoning laser triangulation with laser scanners of the company Götting or the company Pepperl+Fuchs is currently supported, as are the »Jupiter« and »Triton« sensors from the Dutch company Accerion for localization by means of ground features. For outdoor vehicles, a differential GPS receiver from Götting can be used (other sensors/methods on request). Therefore, the navigation controller can work with a wide variety of sensors from different manufacturers.
The navigation controller is also suitable for vehicles with physical line guidance; however, this might be oversized. On the other hand, the option of so-called hybrid navigation could be interesting, i.e. the combination of two navigation/localization principles between which switching-over is performed depending on the situation. An AGV is guided, for example, in long narrow rack aisles by means of an optical guideline; outside of aisles, for example when changing aisles or when driving to manual order picking stations, it drives on a virtual track, e.g. by means of laser navigation.
All common kinematic principles available
A further important aspect in the control of AGV is the vehicle kinematics: since the navigation computer uses dead reckoning to determine the position and as it calculates the speed set points for the driving and steering drives, the software must be able to be adapted to the kinematics of the respective AGV (by appropriate parameters). All common kinematic principles are supported: 3-wheeler and 4-wheeler, with or without geometric steering angle, and with up to 4 individually controlled driving and steering motors.
Cost-efficient according to runtime license fees
The use of the navigation controller software is based on a license model, i.e. a non-exclusive runtime license is granted, which must be paid per AGV equipped with the navigation controller and being used in an industrial environment. Individual adaptations to customer requirements are just as possible and self-evident as training, personal support with the first projects and extensive documentation of the system. For further information, please contact us.
We will also be glad to help you if you want to run several AGVs simultaneously in one system and require a fleet management software. For this purpose, we offer the software openTCS, more details can be found here.
 Fraunhofer Institute for Material Flow and Logistics IML
Fraunhofer Institute for Material Flow and Logistics IML